

At the end of this course, you will be able to:ġ.
#Histogram in word how to
You will also learn the history and context of data science, the skills, challenges, and methodologies the term implies, and how to structure a data science project. Cloud computing, SQL and NoSQL databases, MapReduce and the ecosystem it spawned, Spark and its contemporaries, and specialized systems for graphs and arrays will be covered. You will learn how practical systems were derived from the frontier of research in computer science and what systems are coming on the horizon. In this course, you will learn the landscape of relevant systems, the principles on which they rely, their tradeoffs, and how to evaluate their utility against your requirements. The abstractions that emerged in the last decade blend ideas from parallel databases, distributed systems, and programming languages to create a new class of scalable data analytics platforms that form the foundation for data science at realistic scales. Extracting knowledge from large, heterogeneous, and noisy datasets requires not only powerful computing resources, but the programming abstractions to use them effectively. Some authors recommend that bar charts have gaps between the rectangles to clarify the distinction.Data analysis has replaced data acquisition as the bottleneck to evidence-based decision making - we are drowning in it. A histogram is used for continuous data, where the bins represent ranges of data, while a bar chart is a plot of categorical variables.
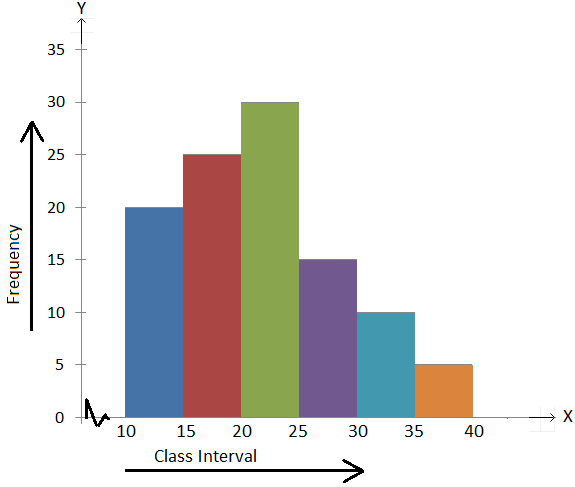
Histograms are sometimes confused with bar charts. The histogram is one of the seven basic tools of quality control. The density estimate could be plotted as an alternative to the histogram, and is usually drawn as a curve rather than a set of boxes.Īnother alternative is the average shifted histogram, which is fast to compute and gives a smooth curve estimate of the density without using kernels. This yields a smoother probability density function, which will in general more accurately reflect distribution of the underlying variable. If the length of the intervals on the x-axis are all 1, then a histogram is identical to a relative frequency plot.Ī histogram can be thought of as a simplistic kernel density estimation, which uses a kernel to smooth frequencies over the bins. The total area of a histogram used for probability density is always normalized to 1. Histograms give a rough sense of the density of the underlying distribution of the data, and often for density estimation: estimating the probability density function of the underlying variable. Examples of variable bin width are displayed on Census bureau data below.Īs the adjacent bins leave no gaps, the rectangles of a histogram touch each other to indicate that the original variable is continuous. It then shows the proportion of cases that fall into each of several categories, with the sum of the heights equaling 1. A histogram may also be normalized displaying relative frequencies. In general, however, bins need not be of equal width in that case, the erected rectangle has area proportional to the frequency of cases in the bin The vertical axis is not frequency but density: the number of cases per unit of the variable on the horizontal axis. If the bins are of equal size, a rectangle is erected over the bin with height proportional to the frequency, the number of cases in each bin. The bins (intervals) must be adjacent, and are usually equal size. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable.
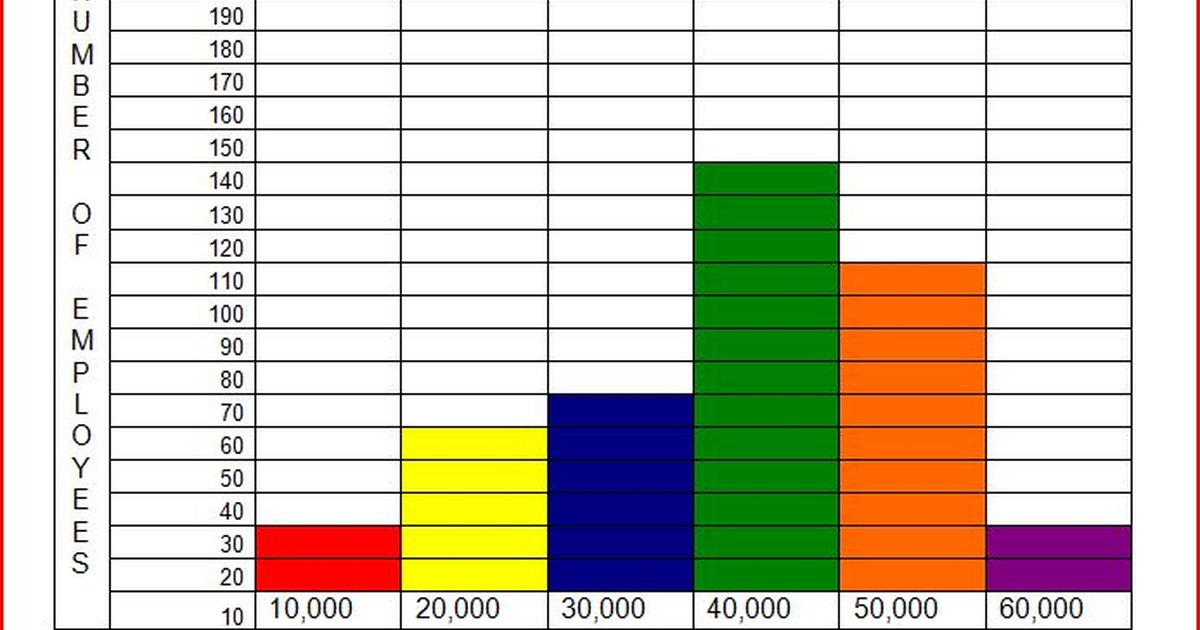

#Histogram in word series
To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" the range of values-that is, divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals-and then count how many values fall into each interval. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable (quantitative variable) and was first introduced by Karl Pearson. A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
